As with vitamin C, deficits in other vitamins and minerals can also precipitate nutritional diseases that adversely impact the brain in humans.
During the long seafaring voyages of the 15th and 16th centuries, a period known as the Age of Discovery, sailors reported experiencing visions of sublime foods and verdant fields. The discovery that these were nothing more than hallucinations after months at sea was agonizing. Some sailors wept in longing; others threw themselves overboard.
As this famous example of early explorers illustrates, there is an intimate connection between food and the brain, one that researchers like me are working to unravel.at the University of Michigan, I am primarily interested in how components of food and their breakdown products can alter the genetic instructions that control our physiology.
For example, low dietary levels of vitamin B3/niacin—typically found in meat and fish—cause pellagra, a disease in which people develop dementia. Another example of how a nutrient deficiency affects brain function can be found in the element iodine, which, like niacin, must be acquired from one’s diet. Iodine, which is present in seafood and seaweed, is an essential building block for thyroid hormones—signaling molecules that are important for many aspects of human biology, including development, metabolism, appetite and sleep.
Researchers think that these diet-dependent changes, especially the higher production of brain chemicals that can quiet down neurons and decrease levels of inflammatory molecules, may play a role in the ketogenic diet’s ability to lower the number of seizures. These changes may also explain the benefits of a ketogenic state—either through diet or fasting—on cognitive function and mood.
High-fat and processed-food diets are also associated with lower cognitive function and memory in humans and animal models as well as a higher incidence of neurodegenerative diseases. However, researchers still don’t know if these effects are due to these foods or to the weight gain and insulin resistance that develop with long-term consumption of these diets.
México Últimas Noticias, México Titulares
Similar News:También puedes leer noticias similares a ésta que hemos recopilado de otras fuentes de noticias.
 Gold mine plays key role in proving dark matter’s existenceResearchers working at the Stawell gold mine want to figure out whether dark matter actually exists.
Gold mine plays key role in proving dark matter’s existenceResearchers working at the Stawell gold mine want to figure out whether dark matter actually exists.
Leer más »
 5 Worst Foods Slowing Your Metabolism — Eat This Not ThatYour metabolism converts what you eat into energy—and these foods are unfortunately doing your body a disservice.
5 Worst Foods Slowing Your Metabolism — Eat This Not ThatYour metabolism converts what you eat into energy—and these foods are unfortunately doing your body a disservice.
Leer más »
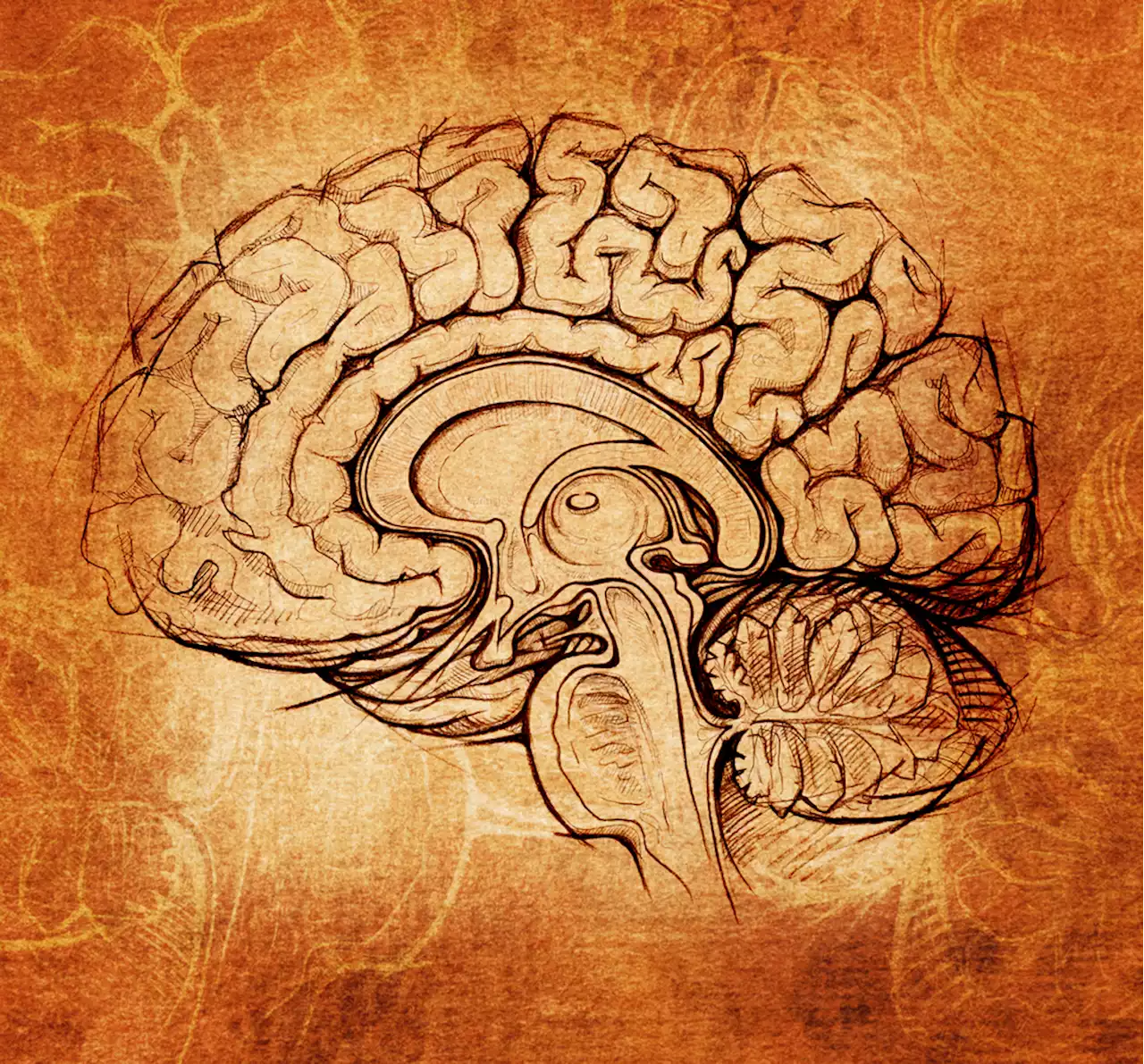 Has There Been a Decrease in Brain Size Among Modern Humans?Decades of research suggest that our brains have shrunk over time, but not all scientists agree.
Has There Been a Decrease in Brain Size Among Modern Humans?Decades of research suggest that our brains have shrunk over time, but not all scientists agree.
Leer más »
 Netflix with ads could cost between $7 and $9 per month | EngadgetNetflix’s forthcoming ad-supported tier could represent a significant discount on the company’s existing plans..
Netflix with ads could cost between $7 and $9 per month | EngadgetNetflix’s forthcoming ad-supported tier could represent a significant discount on the company’s existing plans..
Leer más »
 Ariana Grande Gave Another Rare Glimpse of Her Natural CurlsHer bathtime video clip is so relaxing that I actually got lost in her locks.
Ariana Grande Gave Another Rare Glimpse of Her Natural CurlsHer bathtime video clip is so relaxing that I actually got lost in her locks.
Leer más »
