Scientists reveal new plant cell walls can have significantly different mechanical properties compared to surrounding parental cell walls, enabling cells to change their local shape and influence the growth of plant organs.
This is the first time that scientists have related mechanics to cell wall"age" and was only made possible through a new method that follows the same cells over time and through successive rounds of division.
Research undertaken on two distantly related plant species at the Sainsbury Laboratory Cambridge University provides new evidence suggesting local level cell division has an active role to play in controlling organ size. The interdisciplinary project was a collaboration between three SLCU research teams and the SLCU Microscopy Facilities Team, bringing together expertise in experimental biomechanics, genetics, imaging and computational modelling.
"We have known for some time that the cell wall is a highly dynamic material. New material is added during cell division, while cell wall mechanical properties are modulated during growth to allow walls to undergo significant changes in shape and size without breakage," Dr Bonfanti said.
"The fact that the new cell walls are much stiffer results in organ growth being restricted as it impedes the growth and influences the shape of component cells.cells also change their geometry and develop a 120° junction angle quicker to form cell geometries closer to hexagonal shapes, which are thought to be the most efficient shapes in terms of forming a material to cover an area.
México Últimas Noticias, México Titulares
Similar News:También puedes leer noticias similares a ésta que hemos recopilado de otras fuentes de noticias.
 Scientists Discover Source of Mysterious Alignment of Stars Near the Galactic CenterScientists from The University of Manchester and the University of Hong Kong have found a source for the enigmatic alignment of stars close to the Galactic Center. The initial discovery of the alignment of planetary nebulae was made a decade ago by Bryan Rees, a Manchester PhD student, but has re
Scientists Discover Source of Mysterious Alignment of Stars Near the Galactic CenterScientists from The University of Manchester and the University of Hong Kong have found a source for the enigmatic alignment of stars close to the Galactic Center. The initial discovery of the alignment of planetary nebulae was made a decade ago by Bryan Rees, a Manchester PhD student, but has re
Leer más »
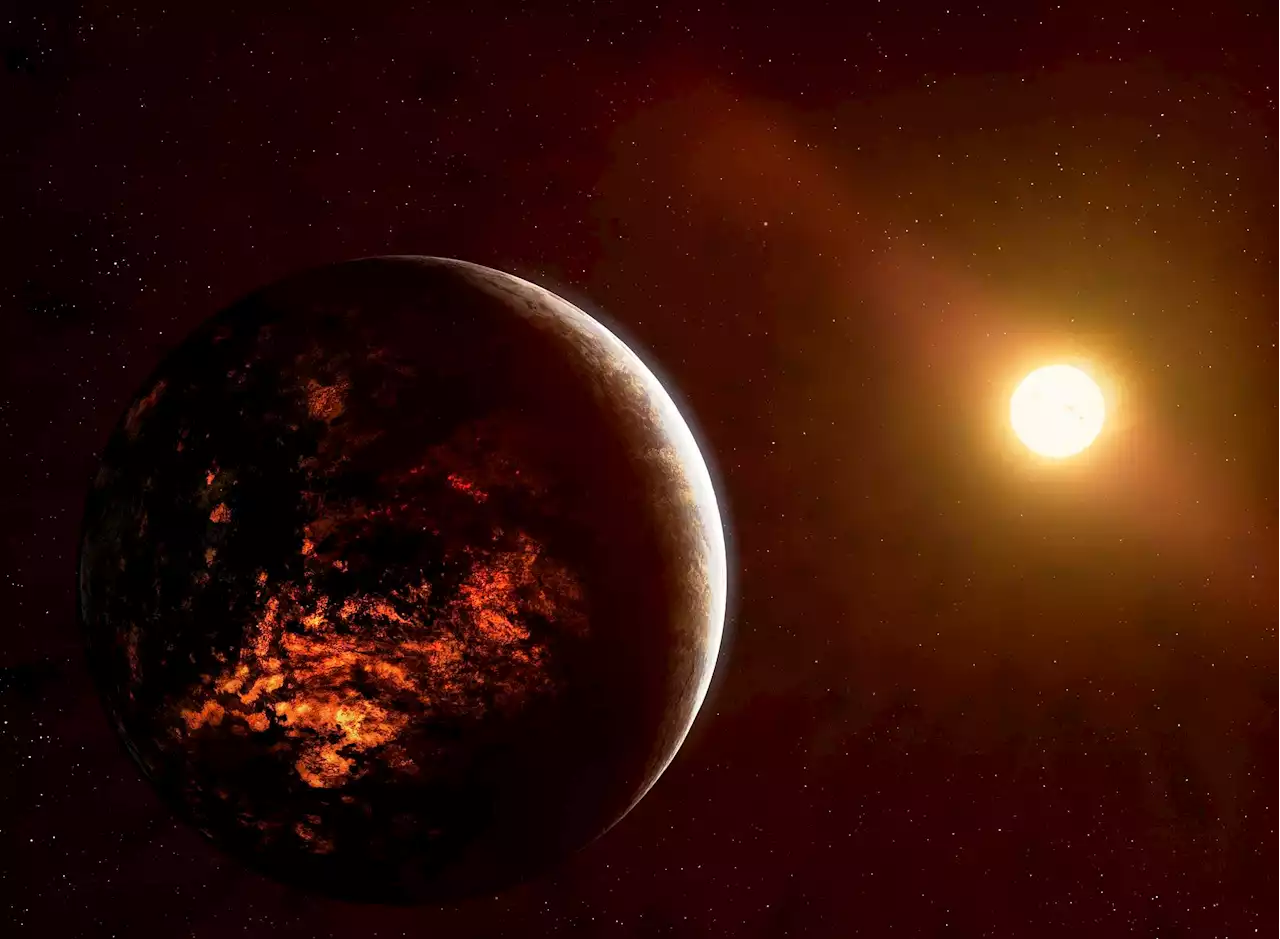 Half Of All Rocky Planets Are Strange ‘Burning Worlds’ Of Lava, Say ScientistsA new study reveals secrets about the mysterious planets where molten lava flows on the surface—one of the most common types of exoplanets so far discovered.
Half Of All Rocky Planets Are Strange ‘Burning Worlds’ Of Lava, Say ScientistsA new study reveals secrets about the mysterious planets where molten lava flows on the surface—one of the most common types of exoplanets so far discovered.
Leer más »
 Brazil's diversity makes country a testing ground for a global stem cell biobank, scientists sayA biobank for all, in which a person from any background could find a bone marrow donor for a stem cell transplant, is a major goal for stem cell science. While repositories of cell lines that could be a match for most patients are successfully materializing in some countries with genetically homogenous populations like Japan and the United Kingdom, how many more we need for a universal solution remains unknown. Researchers estimate at least 559 distinct cell lines would be required to cover 95% of the more diverse, and globally representative, people of Brazil.
Brazil's diversity makes country a testing ground for a global stem cell biobank, scientists sayA biobank for all, in which a person from any background could find a bone marrow donor for a stem cell transplant, is a major goal for stem cell science. While repositories of cell lines that could be a match for most patients are successfully materializing in some countries with genetically homogenous populations like Japan and the United Kingdom, how many more we need for a universal solution remains unknown. Researchers estimate at least 559 distinct cell lines would be required to cover 95% of the more diverse, and globally representative, people of Brazil.
Leer más »
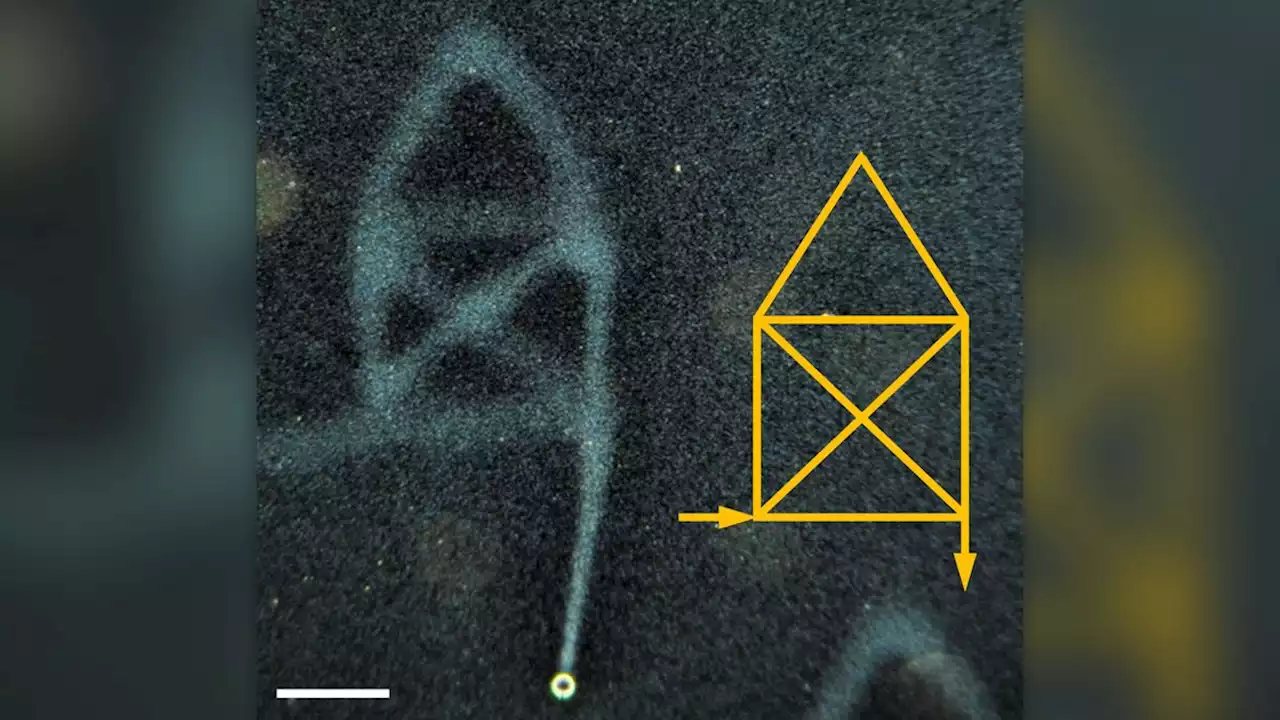 For 1st time, scientists write words in liquid waterScientists used a process called 'diffusioosmosis' to write words that lingered in liquid water.
For 1st time, scientists write words in liquid waterScientists used a process called 'diffusioosmosis' to write words that lingered in liquid water.
Leer más »
 Hungarian and U.S. scientists win medicine Nobel for COVID-19 vaccine workScientists Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman from Hungary and the United States respectively won the 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discoveries enabling the development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the award-giving body said on Monday.
Hungarian and U.S. scientists win medicine Nobel for COVID-19 vaccine workScientists Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman from Hungary and the United States respectively won the 2023 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine for discoveries enabling the development of mRNA COVID-19 vaccines, the award-giving body said on Monday.
Leer más »
 Nobel Prize in medicine awarded to scientists who laid foundation for messenger RNA vaccinesThe Nobel Prize in medicine was awarded to Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman, scientists who worked together to turn messenger RNA from a fragile genetic material that triggered a problematic immune response into a powerful medicine. Their key breakthrough in 2005 went largely unnoticed, but is now the backbone of two leading coronavirus vaccines and could lead to a whole new class of vaccines and drugs.
Nobel Prize in medicine awarded to scientists who laid foundation for messenger RNA vaccinesThe Nobel Prize in medicine was awarded to Katalin Kariko and Drew Weissman, scientists who worked together to turn messenger RNA from a fragile genetic material that triggered a problematic immune response into a powerful medicine. Their key breakthrough in 2005 went largely unnoticed, but is now the backbone of two leading coronavirus vaccines and could lead to a whole new class of vaccines and drugs.
Leer más »
