Researchers hope it could eventually lead to new ways of treating age-related macular degeneration.
"In the past, scientists would grow cells on a flat surface, which is not biologically relevant," Prof Pierscionek said."This an exciting breakthrough that could potentially help millions of people."Mary Davies, 84, from Downham Market in Norfolk, has dry AMD and can no longer drive or teach macramé - a needlework craft."I've known people with a diagnosis who thought it was the end of their lives," she said.
Chief executive Cathy Yelf said: "Macular disease is as prevalent as dementia and represents a huge cost, care and societal burden. "While there still needs to be a lot more work done before we see this being used in humans, this is an encouraging area of research."
México Últimas Noticias, México Titulares
Similar News:También puedes leer noticias similares a ésta que hemos recopilado de otras fuentes de noticias.
 Utah data helps researchers highlight how urbanization impacts wildlifeNorth American cities, including the Salt Lake City area, are getting warmer, and researchers warn the heat is making it more difficult for native wildlife to adjust to the growing urbanization near their homes.
Utah data helps researchers highlight how urbanization impacts wildlifeNorth American cities, including the Salt Lake City area, are getting warmer, and researchers warn the heat is making it more difficult for native wildlife to adjust to the growing urbanization near their homes.
Leer más »
 Researchers create optical device that can kill pathogens on surfaces while remaining safe for humansWhile it has long been known that ultraviolet (UV) light can help kill disease-causing pathogens, the COVID-19 pandemic has put a spotlight on how these technologies can rid environments of germs. However, the excimer lamps and LEDs that can directly emit light in the required deep-UV wavelengths generally have low efficiency or suffer from short lifetimes. Moreover, UV light of the wrong wavelength can actually be harmful to human cells.
Researchers create optical device that can kill pathogens on surfaces while remaining safe for humansWhile it has long been known that ultraviolet (UV) light can help kill disease-causing pathogens, the COVID-19 pandemic has put a spotlight on how these technologies can rid environments of germs. However, the excimer lamps and LEDs that can directly emit light in the required deep-UV wavelengths generally have low efficiency or suffer from short lifetimes. Moreover, UV light of the wrong wavelength can actually be harmful to human cells.
Leer más »
 Researchers improve efficiency in carbon dioxide electroreductionResearchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yanshan University have proposed a strategy for boosting the CO faradaic efficiency in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR), an attractive option to address serious climate concerns and produce value-added chemical feedstock via coupling with renewable energies. The strategy is promising in producing CO via eCO2RR at ambient conditions.
Researchers improve efficiency in carbon dioxide electroreductionResearchers from the Institute of Process Engineering (IPE) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences and Yanshan University have proposed a strategy for boosting the CO faradaic efficiency in electrocatalytic CO2 reduction reaction (eCO2RR), an attractive option to address serious climate concerns and produce value-added chemical feedstock via coupling with renewable energies. The strategy is promising in producing CO via eCO2RR at ambient conditions.
Leer más »
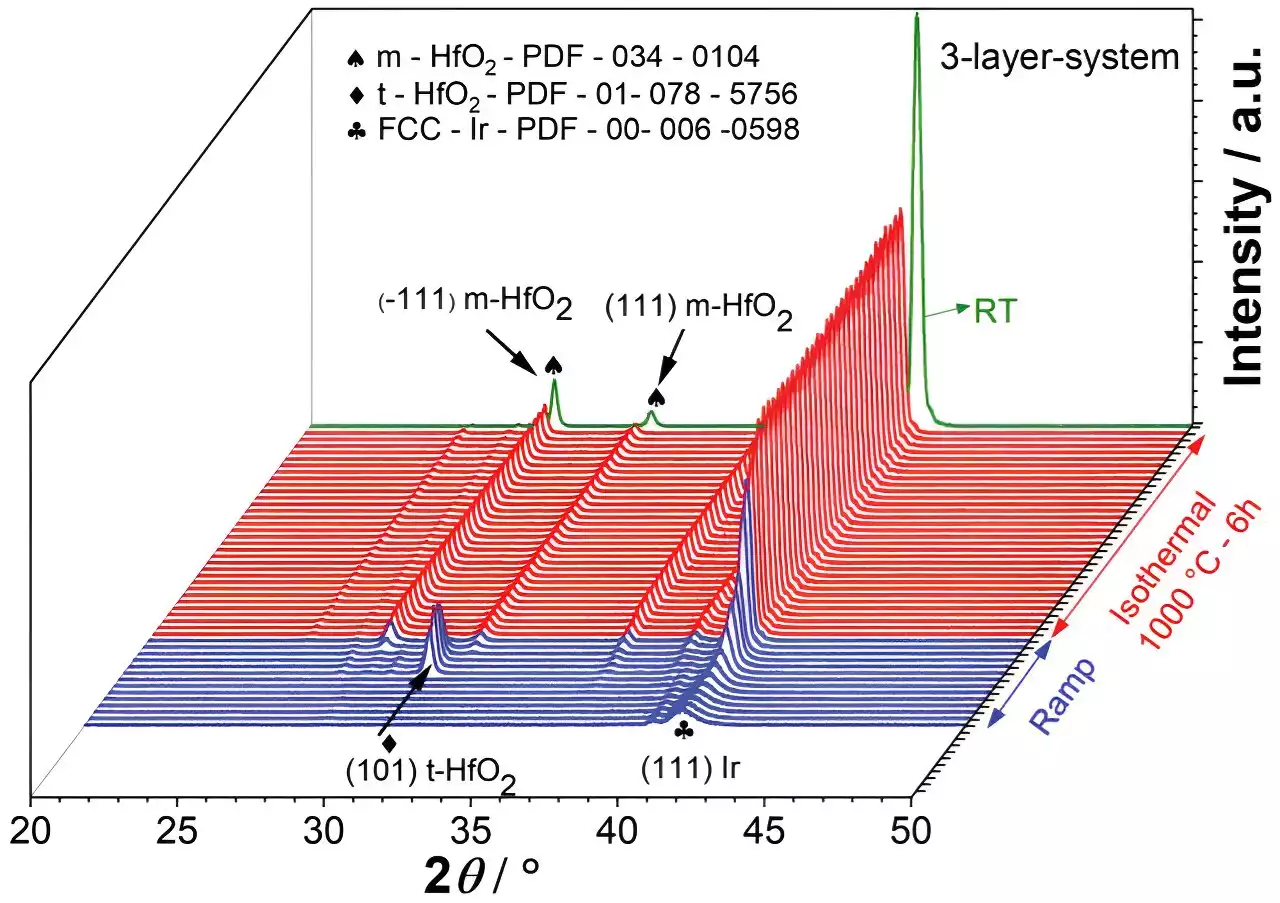 Researchers develop new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaicsResearchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, together with the Technical University of Hamburg and Aalborg University, have developed a new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaics. Iridium was thus used for the first time as a material for an emitter, and in the experiments, it showed particular endurance at high temperatures around 1,000°C. Their study results were published in the journal Advanced Materials and open up new perspectives for producing electricity from heat.
Researchers develop new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaicsResearchers from the Helmholtz-Zentrum Hereon, together with the Technical University of Hamburg and Aalborg University, have developed a new selective emitter based on iridium for thermophotovoltaics. Iridium was thus used for the first time as a material for an emitter, and in the experiments, it showed particular endurance at high temperatures around 1,000°C. Their study results were published in the journal Advanced Materials and open up new perspectives for producing electricity from heat.
Leer más »
 Researchers make a significant step towards reliably processing quantum informationUsing laser light, researchers have developed the most robust method currently known to control individual qubits made of the chemical element barium. The ability to reliably control a qubit is an important achievement for realizing future functional quantum computers.
Researchers make a significant step towards reliably processing quantum informationUsing laser light, researchers have developed the most robust method currently known to control individual qubits made of the chemical element barium. The ability to reliably control a qubit is an important achievement for realizing future functional quantum computers.
Leer más »
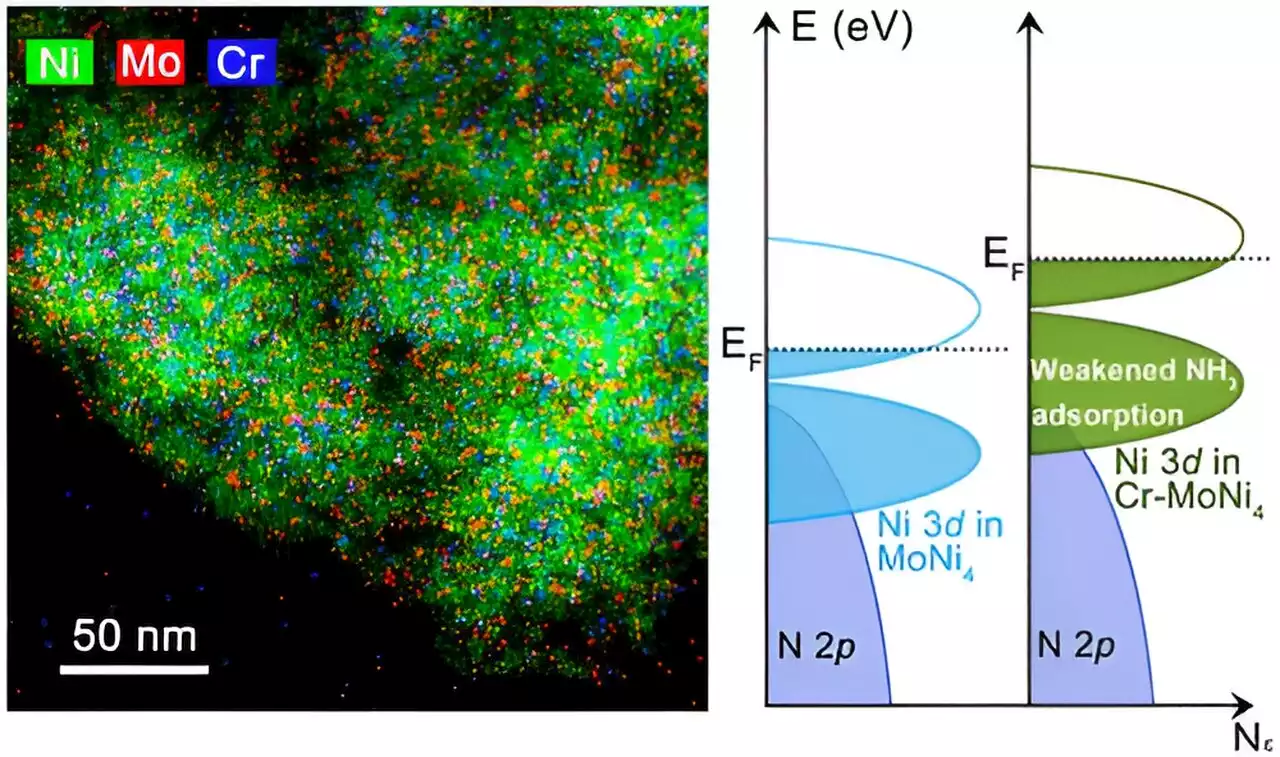 Researchers design ammonia-resistant nickel-based fuel cell catalystA research team led by Prof. Gao Minrui from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a nickel (Ni)-based anion-exchange membrane fuel cell (AEMFC) anode catalyst with high resistance to ammonia (NH3) toxicity. The work was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Researchers design ammonia-resistant nickel-based fuel cell catalystA research team led by Prof. Gao Minrui from the University of Science and Technology of China (USTC) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences has developed a nickel (Ni)-based anion-exchange membrane fuel cell (AEMFC) anode catalyst with high resistance to ammonia (NH3) toxicity. The work was published in Journal of the American Chemical Society.
Leer más »
