Molecules, rare earths, and light: Innovative platform for quantum computers and communications
The ability to interact with light provides important functionalities for quantum systems, such as communicating over large distances, a key ability for future quantum computers. However, it is very difficult to find a material that can fully exploit the quantum properties of light. A research team from the CNRS and l'Université de Strasbourg, with support from Chimie ParisTech-PSL, has demonstrated the potential of a new material based on rare earths as a photonic quantum system.
A team of scientists from the CNRS and l'Université de Strasbourg, with support from Chimie ParisTech-PSL and in collaboration with German teams from KIT, has successfully demonstrated the value of europium molecular crystalsfor quantum communications and processors, thanks to their ultra-narrow optical transitions enabling optimal interactions with light.
Europium molecular crystals represent a major advance, as they have ultra-narrow linewidths. This translates into long-lived quantum states, which were used to demonstrate the storage of a light pulse inside these molecular crystals. Moreover, a first building block for a quantum computer controlled by light has been obtained.
México Últimas Noticias, México Titulares
Similar News:También puedes leer noticias similares a ésta que hemos recopilado de otras fuentes de noticias.
 Unbiasing fermionic quantum Monte Carlo with a quantum computer - NatureA hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for solving many-electron problems is developed, enabling the simulation, with the aid of 16 qubits on a quantum processor, of chemical systems with up to 120 orbitals.
Unbiasing fermionic quantum Monte Carlo with a quantum computer - NatureA hybrid quantum-classical algorithm for solving many-electron problems is developed, enabling the simulation, with the aid of 16 qubits on a quantum processor, of chemical systems with up to 120 orbitals.
Leer más »
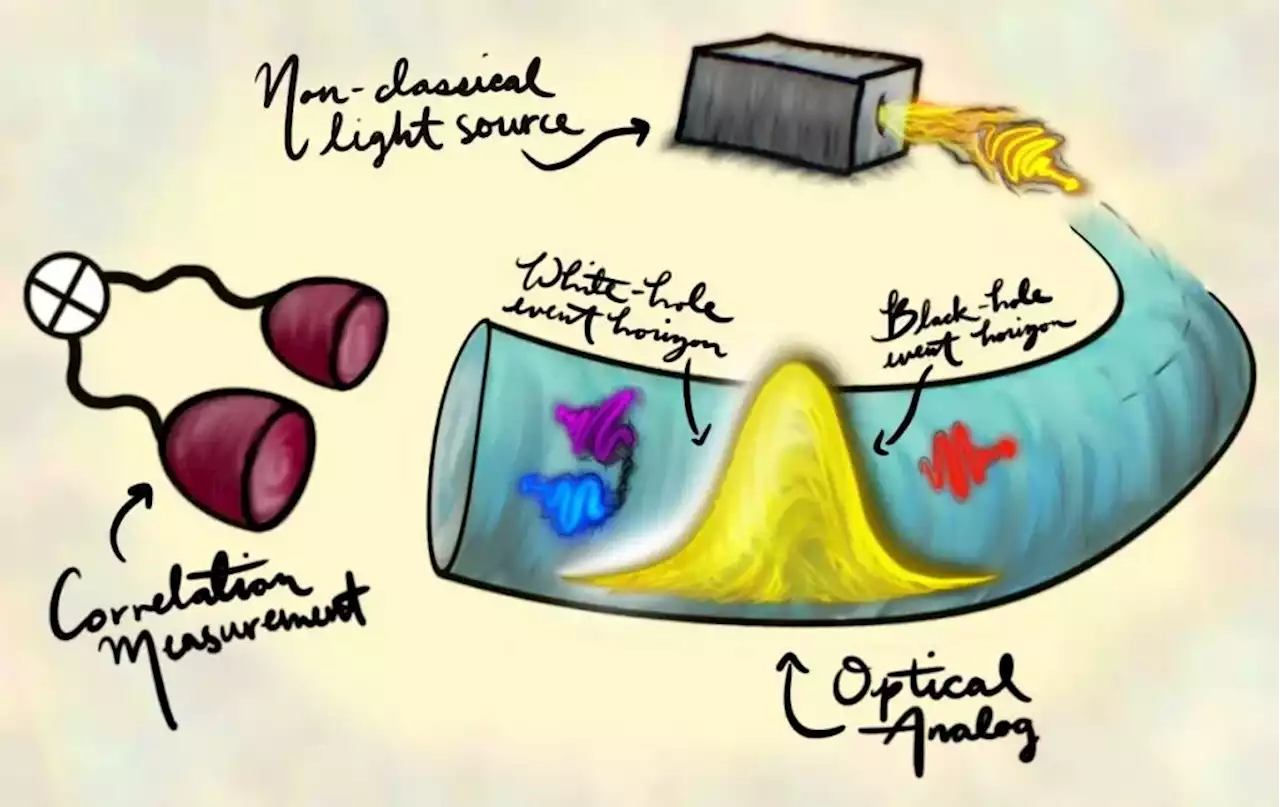 A new way to Confirm Hawking's Idea That Black Holes Give off Radiation - Universe TodayA new way to Confirm Hawking's Idea That Black Holes Give off Radiation: by BrianKoberlein
A new way to Confirm Hawking's Idea That Black Holes Give off Radiation - Universe TodayA new way to Confirm Hawking's Idea That Black Holes Give off Radiation: by BrianKoberlein
Leer más »
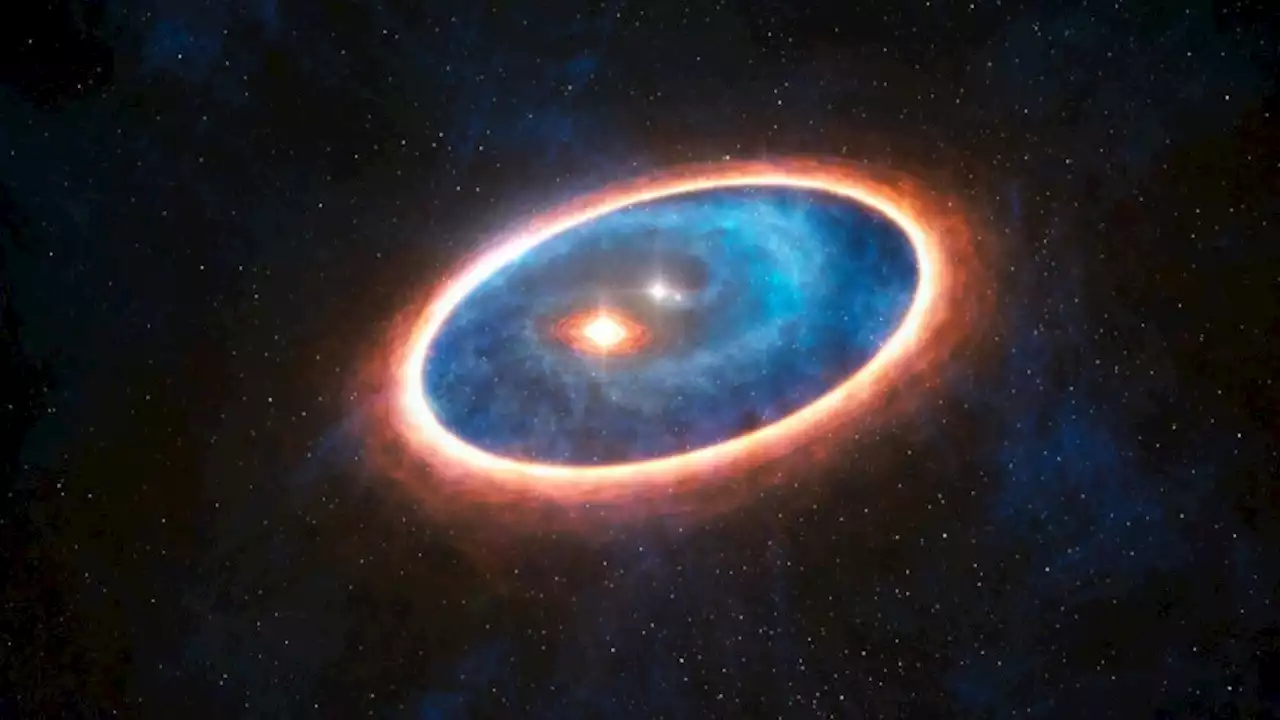 Three separate planetary systems are forming around a binary starThree planetary systems are forming at the same time around a binary star system named SVS 13, 980 light-years away from Earth, according to the findings of astronomers.
Three separate planetary systems are forming around a binary starThree planetary systems are forming at the same time around a binary star system named SVS 13, 980 light-years away from Earth, according to the findings of astronomers.
Leer más »
 Quantum entanglement: A simple explanationQuantum entanglement is one seriously long-distance relationship.
Quantum entanglement: A simple explanationQuantum entanglement is one seriously long-distance relationship.
Leer más »
 Forget mammoths: These researchers are exploring bringing back the extinct Christmas Island rat -- ScienceDailyDinosaurs went extinct 65 million years ago, mammoths 4,000 years ago, and the Christmas Island Rat 119 years ago. Since becoming a popular concept in the 1990s, de-extinction efforts have focused on grand animals with mythical stature, but now a team of paleogeneticists has turned their attention to Rattus macleari, and their findings provide insights into the limitations of de-extinction across all species.
Forget mammoths: These researchers are exploring bringing back the extinct Christmas Island rat -- ScienceDailyDinosaurs went extinct 65 million years ago, mammoths 4,000 years ago, and the Christmas Island Rat 119 years ago. Since becoming a popular concept in the 1990s, de-extinction efforts have focused on grand animals with mythical stature, but now a team of paleogeneticists has turned their attention to Rattus macleari, and their findings provide insights into the limitations of de-extinction across all species.
Leer más »
 Bacterial enzyme makes new type of biodegradable polymerStrings of sugars called polysaccharides are the most abundant biopolymers on Earth. Because of their versatile and environmentally friendly properties, these molecules could eventually replace some plastics. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have identified a previously unknown bacterial enzyme that can make a new type of polysaccharide, which is similar to the biopolymer chitin. The new molecule is biodegradable and could be useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering and other biomedical applications.
Bacterial enzyme makes new type of biodegradable polymerStrings of sugars called polysaccharides are the most abundant biopolymers on Earth. Because of their versatile and environmentally friendly properties, these molecules could eventually replace some plastics. Now, researchers reporting in ACS Central Science have identified a previously unknown bacterial enzyme that can make a new type of polysaccharide, which is similar to the biopolymer chitin. The new molecule is biodegradable and could be useful for drug delivery, tissue engineering and other biomedical applications.
Leer más »
